You have a website with great content, but no one can find it on Google. Technical SEO makes your site easy for search engines to read and understand. Think of it like building a house, you can have beautiful furniture and paint, but if the foundation is weak, the house won’t stand.
Technical SEO strengthens that foundation by fixing the behind-the-scenes parts of your site so Google can crawl, read, and display your pages properly. When done right, search engines find all your pages quickly, understand what each page is about, and show your site to the people looking for what you offer.
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the process of optimizing your website’s technical foundation so search engines like Google can easily find, crawl, and understand your content. It focuses on behind-the-scenes elements like site speed, mobile-friendliness, site structure, XML sitemaps, HTTPS security, and indexing.
Unlike content SEO (which focuses on what you write) or off-page SEO (which focuses on backlinks), technical SEO ensures that search engine crawlers can access all your pages without problems. When your technical SEO is strong, search engines can quickly discover your content, index it properly, and rank it higher in search results.
This leads to more organic traffic, better user experience, and improved rankings. Think of it as building a solid foundation for your house; without it, everything else falls apart, no matter how beautiful the interior is.
Why Technical SEO is the Foundation of Your Website
Your website needs a solid foundation to work well. Technical SEO gives you that foundation.
I learned this the hard way when I first started. I spent weeks writing amazing blog posts, but nobody read them. Why? Because Google couldn’t even find my pages. My site structure was a mess. My pages took forever to load. And I didn’t have an XML sitemap.
Once I fixed these technical problems, things changed fast. My traffic went up by 60% in just two months. The same content, just with a better technical setup.
Think of search engines like guests trying to find their way around your house. If the lights don’t work and the doors are locked, they’ll get frustrated and leave. But when everything works smoothly, they can explore every room easily. That’s what technical optimization does for your site.
How Technical is Different from On-Page and Off-Page SEO
Many people get confused about the different types of SEO. Let me make it simple.
- On-page SEO is about the content people see. This includes your blog posts, product descriptions, images, and titles. You write good content that helps people solve problems.
- Off-page SEO is about what happens outside your website. This means getting other websites to link to you. It’s about building trust and authority online.
- Technical SEO works in the background. It makes sure your website runs fast, loads on phones correctly, and search engines can read all your pages. You don’t see most of this work, but it makes everything else possible.
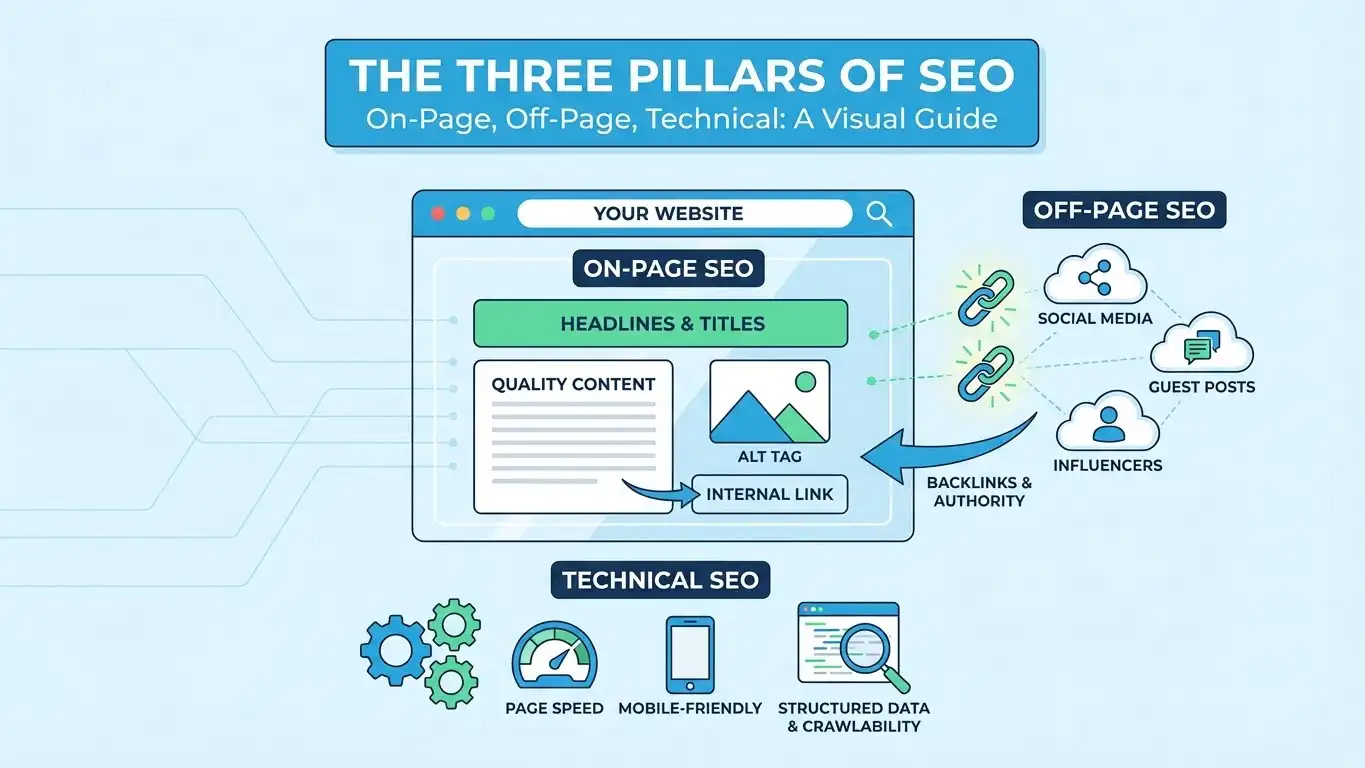
All three types work together. Great content won’t help if Google can’t find it. And backlinks won’t help if your site is broken. You need all three to succeed.
Why Technical SEO Matters for Your Website
Many business owners ask me, “Why should I care about technical SEO?” The answer is simple; it directly affects how much money you make online.
Search engines like Google have rules. If your website follows these rules, you get better rankings. Better rankings mean more people see your website. More visitors mean more customers and sales.
According to a study published by BrightEdge, organic search drives 53% of all website traffic. That’s more than half of your potential customers. But here’s the catch: they can only find you if your technical SEO is good.
When your website speed is slow, people leave before your page loads. Google sees this and drops your ranking. When your site doesn’t work on mobile devices, you lose even more visitors. About 60% of searches now happen on phones, according to Statista.
I once worked with a client who had this problem. Their website looked great on computers but was terrible on phones. They were losing 70% of their visitors. After fixing their mobile-friendliness, their sales doubled in three months.
Helps Search Engines Find Your Content
Google uses programs called crawlers or spiders to find websites. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, like a spider moving across its web.
But crawlers can get stuck. If your robots.txt file blocks them, they can’t see your pages. If your site structure is confusing, they might miss important pages. When pages take too long to load, crawlers might give up and move to another site.
Your job is to make crawling easy. Use internal links to connect your pages. Create an XML sitemap to show crawlers all your pages. Fix any broken links that lead nowhere.
When crawlers can explore your entire site easily, all your pages get into Google’s index. This means your pages can show up when people search. More pages in the index mean more chances to be found.
Better Rankings Mean More Visitors
Here’s what happens when you fix technical SEO problems:
Your pages load faster. Google notices this and moves you up in search results. More people click on your site because you’re at the top. These visitors stay longer because your site works well. And Google sees this positive signal, which helps you rank even higher.
It’s like a good cycle that keeps getting better.
One of my websites was stuck on page 3 of Google for months. I improved the page speed from 6 seconds to 2 seconds. Within two weeks, I jumped to page 1. My traffic went from 50 visitors per day to 400 visitors per day.
The content didn’t change at all. Only the technical parts changed. But the results were amazing.
Understanding How Search Engines Work
To do good technical SEO, you need to understand what search engines do. It’s actually pretty simple when you break it down.
Search engines have three main jobs: crawling, indexing, and ranking. Each step is important.
First, they crawl websites to find new pages. Then they index these pages by storing information about them. Finally, they rank pages based on how useful and relevant they are.
What is Crawling and Why Does it Matter?
Crawling is when search engines send out bots to explore the internet. These bots are called crawlers, spiders, or bots. They visit web pages and follow every link they find.
Think of it like this: You’re at a party, and you know one person. That person introduces you to their friends. Those friends introduce you to more people. Soon you’ll have met everyone at the party. Crawlers work the same way; they follow links from page to page.
But crawlers have limits. They can’t spend forever on one website. They have a crawl budget, which means they only have so much time to spend on your site. If your site is slow or has too many pages, crawlers might not see everything.
This happened to me once. I had a website with 5,000 pages. But Google was only crawling 500 of them. The other pages were too deep in my site structure. I fixed this by improving my internal linking and creating better navigation. Within a month, Google found all my pages.
To help crawlers, make your site easy to explore. Use simple URL structures. Connect your pages with good internal links. And don’t hide important pages behind forms or logins, crawlers can’t access those.
How Indexing Works
After crawlers visit your pages, the next step is indexing. This is when Google saves information about your page in its huge database.
Google looks at everything on your page. It reads your content, checks your images, and sees how your page is built. Then it stores this information so it can show your page when someone searches.
But not all pages get indexed. Google only indexes pages it thinks are useful. If your page has thin content, duplicate content, or a noindex tag, Google will skip it.
I remember setting up a new website and wondering why it wasn’t showing up in Google. After checking Google Search Console, I found out my pages had noindex tags. I was accidentally telling Google not to index them! Once I removed those tags, my pages showed up in search results within days.
You can check which of your pages are indexed by using Google Search Console. This free tool shows you exactly what Google sees on your site. It tells you if there are problems and how to fix them.
Key Elements of Technical SEO
Now let’s talk about the most important parts of technical SEO. These are the things that make the biggest difference.
Website Speed and Performance
Page speed is one of the most important ranking factors. Google has said this many times. Fast sites rank higher. Slow sites rank lower.
But it’s not just about rankings. People hate slow websites. Studies show that 53% of mobile users leave a site if it takes more than 3 seconds to load, according to Google’s research.
I’ve seen this with my own sites. When I reduced my loading time from 5 seconds to 2 seconds, my bounce rate dropped by 40%. People stayed longer. They visited more pages. And my sales went up.
There are many ways to make your site faster:
- Compress your images so they’re smaller. Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim. Big image files are the number one reason sites are slow.
- Enable browser caching so returning visitors don’t have to download everything again.
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to serve your content from servers close to your visitors.
- Minify your code by removing extra spaces and characters from your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
These might sound technical, but they’re not that hard. Many hosting companies and plugins can do this for you automatically.
Core Web Vitals You Should Know
In 2021, Google introduced Core Web Vitals. These are three specific metrics that measure user experience.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures how long it takes for the main content to load. Google wants this to happen in 2.5 seconds or less.
- First Input Delay (FID) measures how quickly your site responds when someone clicks a button. This should be under 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures how much your page jumps around while loading. We’ve all been on sites where you try to click something, but the page shifts and you click the wrong thing. That’s bad, CLS.
You can check these metrics using PageSpeed Insights, a free tool from Google. Just enter your URL, and it shows you exactly how you’re doing.
When I first checked my site, my LCP was 4.5 seconds, way too slow. After optimizing my images and using better hosting, I got it down to 2.1 seconds. My rankings improved within two weeks.
Mobile-Friendly Websites
More than half of all web traffic comes from mobile devices like phones and tablets. If your site doesn’t work well on mobile, you’re losing money.
I learned this lesson years ago. I had a beautiful website that looked perfect on my computer. But when I checked it on my phone, it was a disaster. The text was too small. Buttons were impossible to click. Images were cut off.

My mobile traffic was only 5% of my total traffic, way below normal. After making my site mobile-friendly, that jumped to 58%. And my total traffic doubled because mobile users could finally use my site.
Responsive design is the solution. This means your website automatically adjusts to fit any screen size. The same website works on computers, tablets, and phones. You don’t need separate versions.
Most modern website themes and builders include responsive design. But you should still test your site. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check if your site passes.
Why Mobile-First Indexing is Important
Google now uses mobile-first indexing. This means Google looks at the mobile version of your site first when deciding how to rank you.
Even if most of your visitors use computers, Google still checks your mobile site first. If your mobile site is broken or missing content, your rankings will suffer, even on desktop searches.
Make sure your mobile site has all the same content as your desktop site. Don’t hide things on mobile just to save space. Google needs to see everything.
Check that your site speed on mobile is good. Mobile networks are often slower than home wifi, so speed matters even more.
Test all your buttons and forms on mobile devices. Make sure everything works. I’ve seen sites where contact forms didn’t work on phones; imagine how many customers they lost!
Site Architecture and Structure
Site architecture is how your pages are organized and connected. Good architecture helps both search engines and visitors find what they need.
Think of your website like a library. Books need to be organized in a logical way. Fiction books go together. History books go together. And there’s a clear system so people can find anything quickly.
Your website needs the same kind of system. Group similar pages together. Make it easy to go from one page to another. And don’t bury important pages where nobody can find them.
Creating a Clear Website Structure
A good website structure follows a simple pyramid shape. Your homepage is at the top. Below that are your main category pages. And below those are individual pages and posts.
Try to keep things simple. Every page on your site should be reachable in three clicks or less from your homepage. This is called shallow depth. If pages are buried too deep, search engines and visitors might never find them.
I once helped a client whose blog posts took seven clicks to reach from the homepage. Google wasn’t indexing most of them. We reorganized the site to make everything accessible in three clicks. Within a month, Google indexed 90% more pages.
Use clear navigation menus to show people where they are and where they can go. Breadcrumbs are helpful too, those little links that show “Home > Blog > Article Title.” They help people and search engines understand your site’s structure.
Avoid orphan pages, pages with no links pointing to them. These pages are invisible to search engines because crawlers can’t find them. Every page needs at least one link from somewhere else on your site.
Internal Links Connect Your Pages
Internal links are links from one page on your site to another page on your site. They’re super important for technical SEO.
Internal links help search engines discover all your pages. When a crawler lands on your homepage, it follows your internal links to find other pages. The more links pointing to a page, the easier it is to find.
Internal links also pass link equity (sometimes called “link juice”). This is a value that flows from page to page through links. Pages with more internal links pointing to them tend to rank better.
But don’t just add random links everywhere. Your internal links should make sense. Link to related content that actually helps your readers. If you’re writing about technical SEO, link to articles about site speed or XML sitemaps.
Use descriptive anchor text, the clickable words in a link. Instead of “click here,” use something like “learn about XML sitemaps.” This helps search engines understand what the linked page is about.
XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt
These two files are essential for technical SEO. They tell search engines which pages to crawl and which pages to skip.
What is an XML Sitemap?
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages on your website. It’s like a map that shows search engines where everything is.
Your sitemap makes it easier for search engines to find and index all your pages. This is especially important for large sites, new sites, or sites with pages that aren’t well-connected through internal links.
Most websites should have an XML sitemap. You can usually find yours at yoursite.com/sitemap.xml. If you don’t have one, don’t worry; most website platforms can create one automatically.
Once you have a sitemap, submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. This tells search engines about your sitemap so they can use it to crawl your site better.
Update your sitemap whenever you add new pages or make big changes. Search engines will check your sitemap regularly, but you can also resubmit it manually to speed things up.
Using Robots.txt the Right Way
Your robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which parts of your site they can visit. You can find this file at yoursite.com/robots.txt.
Be very careful with robots.txt! I’ve seen people accidentally block their entire website from search engines. One wrong line can make your site invisible to Google.
Use robots.txt to block pages that don’t need to be indexed. This might include admin pages, duplicate versions of pages, or low-value pages like your shopping cart.
But never block important pages that you want to rank in search results. And don’t block your CSS or JavaScript files, Google needs these to understand your site properly.
If you’re not sure what to put in your robots.txt file, it’s better to keep it simple. Many sites do fine with just a basic robots.txt file or even without one.
HTTPS and Website Security
Security matters for SEO. Google has confirmed that HTTPS is a ranking signal. Secure sites rank better than non-secure sites.
Why Secure Websites Rank Better
HTTPS means your website has a secure connection. It encrypts data between your server and your visitors’ browsers. This protects sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers.
You can tell if a site uses HTTPS by looking at the URL. Secure sites start with “https://” and show a lock icon in the browser. Non-secure sites start with “http://” and may show a “Not Secure” warning.
Google wants to keep users safe. That’s why they favor secure sites. If two sites are otherwise equal, the one with HTTPS will rank higher.
But HTTPS isn’t just about rankings. People trust secure sites more. When visitors see that lock icon, they feel safer. They’re more likely to buy from you or share their information.
Getting an SSL Certificate
To use HTTPS, you need an SSL certificate (or TLS certificate, they’re basically the same thing). This certificate proves your site is secure.
Many web hosting companies now include free SSL certificates. Check with your host; you might already have one available.
If you need to get a certificate yourself, Let’s Encrypt offers free SSL certificates. Paid certificates are available, too, if you want extra features.
After you install your certificate, make sure to set up 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS. This sends visitors and search engines to the secure version of your site.
Then update all your internal links to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. This prevents mixed content warnings and makes sure everything is fully secure.
Fixing Common Technical SEO Problems
Even good websites have technical problems. The key is finding and fixing them quickly.
Broken Links and 404 Errors
Broken links point to pages that don’t exist anymore. When someone clicks a broken link, they see a 404 error page that says “Page Not Found.”
These errors hurt user experience. Imagine clicking a link and getting an error instead of the information you wanted. Frustrating, right? Search engines don’t like this either.
Broken links also waste your crawl budget. Crawlers follow these links, find nothing, and move on. That’s time they could have spent crawling real pages.
Check your site regularly for broken links. Tools like Screaming Frog or the Site Audit in Google Search Console can find them for you.
When you find broken links, you have a few options. If the page moved to a new URL, set up a 301 redirect to send people to the new location. If the page is gone forever, remove links to it or replace them with links to similar content.
I check my sites for broken links every month. Last time I found 15 broken links I didn’t know about. After fixing them, my crawl efficiency improved, and Google indexed more of my pages.
Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content means the same or very similar content appears on multiple pages. This confuses search engines. They don’t know which version to show in search results.
Common causes of duplicate content include printer-friendly versions of pages, products that appear in multiple categories, HTTP and HTTPS versions of the same page, and WWW and non-WWW versions of the same page.
Google won’t penalize you for duplicate content, but it can hurt your SEO. Search engines might pick the wrong version to rank. And your link equity gets split between duplicate pages instead of focusing on one page.
Use canonical tags to fix duplicate content. These tags tell search engines which version of a page is the original. The canonical tag goes in the HTML of duplicate pages and points to the preferred version.
For example, if you have a product that appears in three different categories, all three pages should have a canonical tag pointing to one main product page.
Schema Markup and Structured Data
Schema markup is code that helps search engines understand your content better. It’s like giving search engines extra information about what your page contains.
What is Schema Markup?
When you add structured data to your pages, you’re telling search engines exactly what kind of content you have. Is it a recipe? A product? A local business? An event?
This extra information helps search engines show rich results or rich snippets in the search results. These are the special search results with star ratings, prices, images, or other extra details.
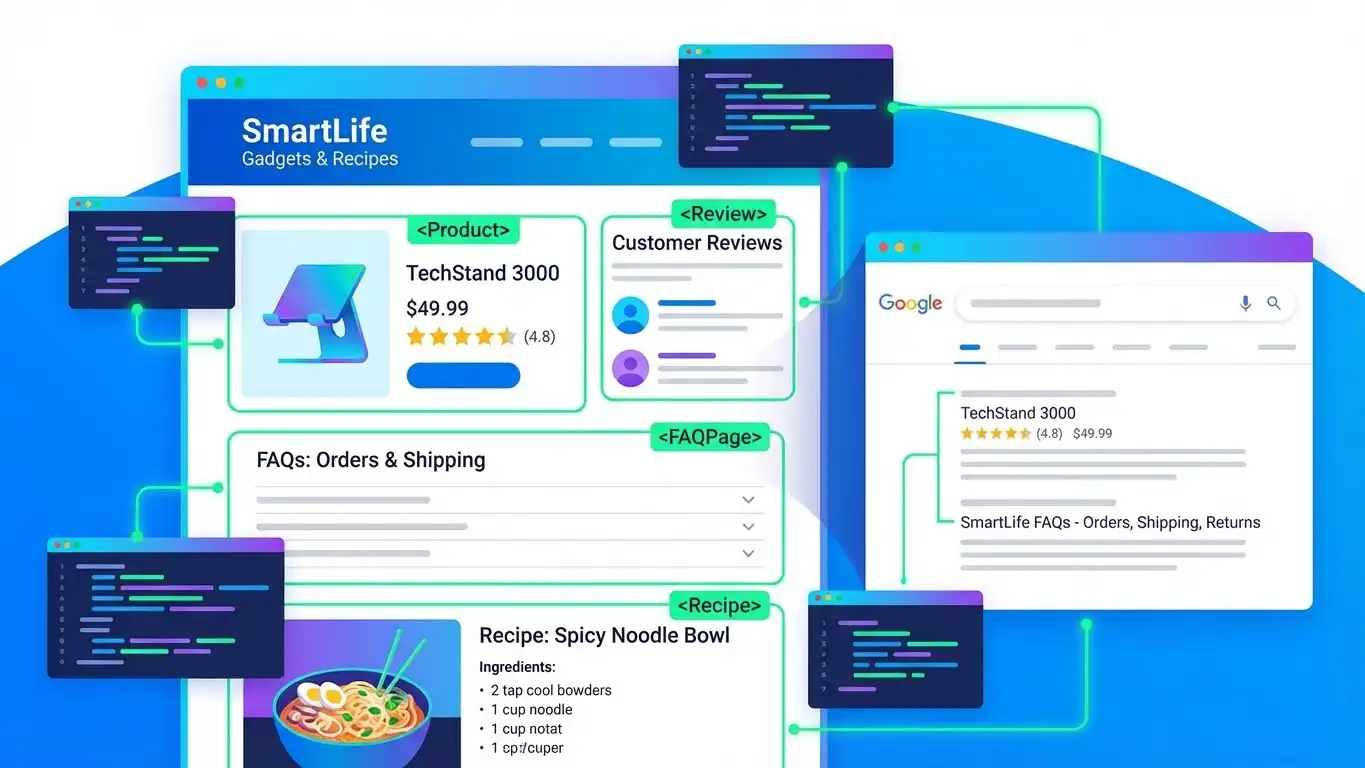
Rich snippets stand out in search results. They get more attention and more clicks. Research shows that pages with rich snippets can see click-through rates increase by 30% or more.
I added recipe schema to my cooking blog. My pages started showing up with photos, ratings, and cooking times right in the search results. My traffic increased by 45% in two months.
How to Add Structured Data to Your Site
Adding schema markup might sound technical, but it’s easier than it seems—you don’t need to be a programmer. Start by deciding which type of schema fits your pages. Google’s Structured Data Gallery shows all the options.
Common schema types include:
| Schema Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Product schema | For e-commerce pages |
| Recipe schema | For food blogs |
| FAQ schema | For pages that answer questions |
| Review schema | For customer reviews |
| Local business schema | For local companies |
You can use tools like Schema Markup Generator to create the code easily. Just enter your content info, and the tool generates the code for you.
Next, add the code to your page’s HTML. If you’re on WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO can handle this automatically.
Finally, test your schema with Google’s Rich Results Test. It shows whether your markup is working and previews the rich results your pages might get.
Final Thoughts
Technical SEO is all about making your website work better, faster, mobile-friendly, and easy for search engines to understand. Start with basics like improving speed, fixing broken links, creating an XML sitemap, and checking mobile usability.
Even small fixes can have a big impact: websites can go from barely visible to attracting thousands of visitors just by strengthening their technical foundation. Remember, it’s ongoing, monitor your site regularly with tools like Google Search Console and PageSpeed Insights. Good technical SEO ensures your content gets found, bringing more visitors, customers, and success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between technical SEO and regular SEO?
Regular SEO covers everything to rank higher, like content and backlinks. Technical SEO is part of it, focusing on your site’s speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability, basically, your website’s foundation.
How long does it take to see results from technical SEO?
Small fixes like page speed or broken links can show results in a few weeks. Bigger changes, like site restructuring, usually take 2–3 months. Most sites see noticeable improvements within 30–60 days.
Can I do technical SEO myself?
Yes, for basic tasks like sitemaps, page speed, and fixing broken links. Tools like Google Search Console and PageSpeed Insights help. For complex issues like server setup or large migrations, consider an expert.
What tools can I use for technical SEO?
Key tools include Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, Screaming Frog, GTmetrix, and Mobile-Friendly Test. Most are free and cover everything you need to improve your site.
Is technical SEO a one-time task?
No, it requires ongoing maintenance. Check your site monthly for broken links, speed issues, and crawl errors. Major updates like redesigns need careful planning. Regular upkeep keeps your site healthy.